French Politics – part II -
Institutions
VI. French Political Institutions – President, Parliament, Prime Minister, Cabinet, Party System
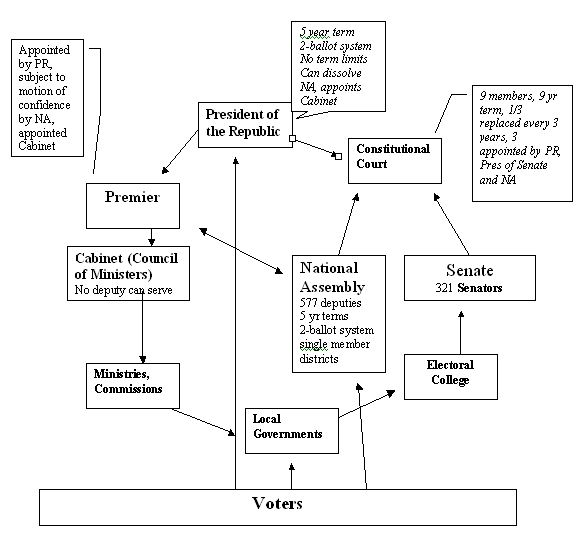
Model of French Political Institutions
A. French Constitution – 5th Republic
1.
Written – product of DeGaulle’s ascension to the Presidency in 1958-59
2. Republican
3. Limited Parliamentary sovereignty – Parliament checked by both the
President and the
Constitutional Council
4.
Semi-Presidential - dual
executive with Premier accountable both to the legislature
and to the President of the
Republic (Note: Kesselman refers to “Triple Executive”)
a. Limited separation of powers between executive, legislature
i.
No dual membership in executive and legislature
ii.
President appoints
Premier, dissolves National Assembly Art 12
1. Only one dissolution per year Art 12
2. Premier/Government can be subject to motion of censure
a. Signed by tenth of deputies, only favorable votes
counted, must have majority of all deputies (289) Art 49
b. Govt. can make passage of a bill “an issue of
responsibility” – the bill is passed unless a motion of censure is passed
iii.
President/Premier
collaborate in appointment of Cabinet Art 8
1. PR “appoints civil and military posts of the State.”
Art 13
2. Premier “shall make appointments to civil and military
posts” Art 21
iv.
President presides
over Council of Ministers Art 9
v.
President can submit bills
to referendum Art 11
vi.
Refer bills to
Constitutional Council
vii.
President as
commander in chief - negotiate and ratify treaties, controls
nuclear forces Art 15
b. Parliament
i.
2 houses: National
Assembly and Senate
ii.
Pass “statutes” dealing with: (art 34)
1. Civic rights, public liberties
2. Nationality, legal status of persons, inheritance,
etc.
3. Determination of serious crimes/penalties
4. Criminal procedure, amnesties, est. of Courts
5. Taxes, currency
6. Rules dealing:
a. Parliamentary and local assemblies
b. Public establishments
c. Guarantees to civil and military State personnel
d. Nationalization of firms
e. General organization of national defense
f. Self government of territorial units
g. Education
h. Ownership rules
i.
Labor law, trade union
law
j. Social security
k. Financial acts (Budgets)
iii.
Meets from October to
June, 120 day session
iv.
National Assembly – dominant house, popularly elected
1. 5 year term
2. Led by President of National Assembly (appoints 3
members of CC)
3. Passes motions of censure
4. Government bills take precedence
a. Bills normally are passed in both NA and Senate
i.
If incongruent bills,
joint committee established
ii.
If Senate and NA don’t
agree
1. Government can resubmit to NA for passage anyway…
5. Questions to govt once a week
6. 6 committees
process legislation
a. the Cultural, Family and Social Affairs Committee
(140);
-the Foreign Affairs Committee; (70)
-the National Defence and Armed Forces Committee; (70)
-the Finance, General Economy and Planning Committee; (70)
-the Constitutional Acts, Legislation and General Administration Committee; (70)
-the Production and Trade Committee. (140)
7. Political Groups – min. of 20 deputies common
affiliation
8. Parliamentary Delegations – EU, Demographics,
Planning, Science/Technology, Evaluation of Legislation
v.
Senate – represents local government, indirectly elected
1. Led by President of Senate
(appoints 3 members of CC, temporarily replaced PR if latter is incapacitated)
2. Has 321 members elected by local government members
via an electoral college
(9 yr. Terms, complex elections every 3 yrs, 100 “departments”)
3. Form political groups based on political affiliation
4. Other than fact that NA can override Senate,
legislative process is similar to NA (with 6 committees).
c. Constitutional Committee